Consult a dermatologist before using Retin-A without a prescription. They can assess your skin type and concerns, and determine the appropriate strength and application method.
Understanding Retin-A: Retin-A, containing tretinoin, is a retinoid derived from vitamin A. It treats acne by unclogging pores, reducing inflammation, and speeding cell turnover. It’s also used to minimize wrinkles and improve skin texture.
Potential Risks: Retin-A can cause dryness, redness, and peeling. Sun sensitivity increases significantly; daily sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher is mandatory. Pregnancy and breastfeeding require physician consultation before use.
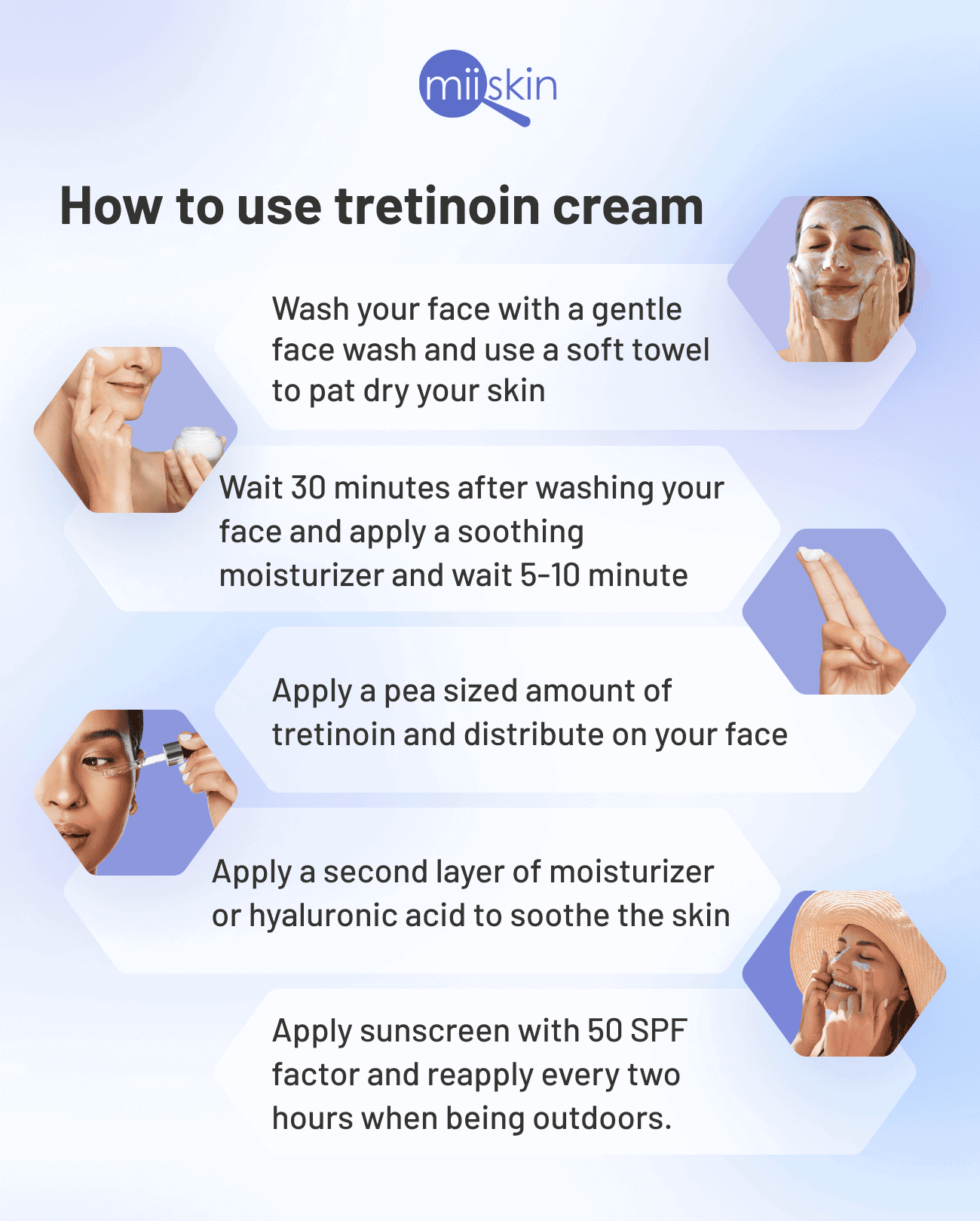
Application Tips: Start with a pea-sized amount, applying thinly to clean, dry skin at night. Avoid the eye area. Gradually increase frequency as your skin tolerates it. Avoid using harsh cleansers or exfoliants simultaneously.
Alternatives: Over-the-counter retinol products offer milder retinoid effects. However, they may require longer use to achieve similar results. Consider retinol as a gentler option before trying Retin-A.
Finding a Doctor: Many online platforms offer telehealth dermatology consultations. These services allow you to have a virtual consultation and potentially obtain a prescription if deemed appropriate. Thoroughly research options, ensuring they’re licensed and reputable.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before starting any new treatment.